How To Troubleshoot BotDetect ASP Classic CAPTCHA Problems (BotDetect ASP v4.x; discontinued)
To help debug any issues you might encounter when integrating BotDetect Classic ASP Captcha in your Classic ASP forms, BotDetect includes a simple troubleshooting helper.
You can also see how it was implemented in the Captcha troubleshooting code example included in BotDetect Classic ASP installations.
How To Activate BotDetect ASP Classic Troubleshooting
To turn BotDetect ASP troubleshooting on, you only have to:
- Copy the
BotDetectDebug.aspfile from your BotDetect ASP Captcha installation folder to your application root (where you copied theBotDetect.aspfile earlier). - Display the result of the Captcha object
Troubleshootingfunction on your form.
BotDetectDebug.asp
The file that needs to be copied is located at C:\Program Files\Captcha Inc\BotDetect 4 CAPTCHA Component\Asp\CaptchaLibrary\BotDetectDebug.asp by default.
It's not recommended to copy this file to your ASP application unless you are currently debugging, and it should be deleted or moved to a protected location afterwards.
While this file is located in your ASP application folder and available to web visitors, it could potentially be used by malicious visitors to bypass any Captcha protection, since among other details it also displays the persisted Captcha codes.
[back to Troubleshooting activation]
Captcha.Troubleshooting
Assuming you added a Captcha object instance to your Classic ASP form by using:
<% Dim TroubleshootingCaptcha : Set TroubleshootingCaptcha = (New Captcha)("TroubleshootingCaptcha") TroubleshootingCaptcha.UserInputID = "CaptchaCode" TroubleshootingCaptcha.Locale = "en-CA" TroubleshootingCaptcha.CodeLength = 4 TroubleshootingCaptcha.CodeStyleName = "Numeric" TroubleshootingCaptcha.ImageStyleName = "Fingerprints" TroubleshootingCaptcha.ImageWidth = 200 TroubleshootingCaptcha.ImageHeight = 80 TroubleshootingCaptcha.ImageFormatName = "gif" TroubleshootingCaptcha.SoundStyleName = "Pulse" TroubleshootingCaptcha.SoundFormat = 1 TroubleshootingCaptcha.SoundFormatName = "WavPcm8bit8kHzMono" Response.Write TroubleshootingCaptcha.Html %>Troubleshooting info can be shown by simply adding:
<% Dim TroubleshootingCaptcha : Set TroubleshootingCaptcha = (New Captcha)( "TroubleshootingCaptcha") TroubleshootingCaptcha.UserInputID = "CaptchaCode" ... Response.Write TroubleshootingCaptcha.Html ... Response.Write TroubleshootingCaptcha.Troubleshooting %>
You don't have to add it immediately after the Html function output, it can be placed anywhere below on the form. The resulting output will look similar to this:
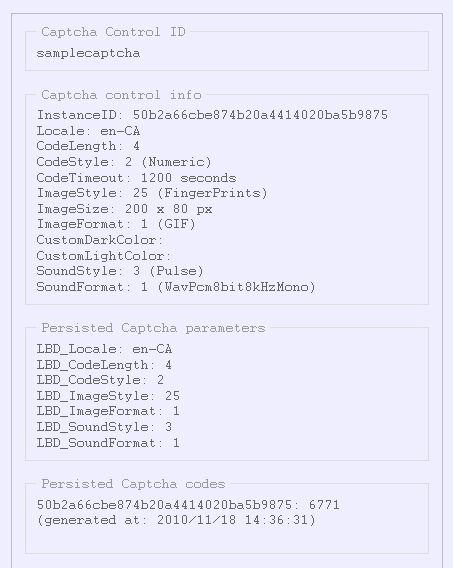
We'll explain the displayed troubleshooting information in the next section.
How To Read BotDetect ASP Classic Troubleshooting Information
The BotDetect ASP Classic troubleshooting output contains the following information:
- Captcha ID
- Current Captcha object instance information
- Persisted Captcha parameters for the current Captcha ID
- Persisted Captcha codes for the current Captcha ID
Captcha ID
This is the identifier you gave to the Captcha object when placing it on the form. If you have multiple Captcha objects placed on different forms within the same ASP application, they should have different Captcha ID values, since all Captcha information is persisted using the normalized Captcha ID value as key ("examplecaptcha" in the screenshot above).
Non-Ascii characters and case are ignored when normalizing Captcha ID values for persistence purposes, so you should avoid using non-Ascii characters and character case to distinguish between Captcha objects.
[back to Troubleshooting info legend]
Current Captcha Object Instance Information
This section displays current Captcha object instance properties.
InstanceID
Each Captcha object instance has an auto-generated unique identifier, which is used to store Captcha codes for separate page loads. This enables Captcha validation to work properly when the form is open in multiple browser tabs at once, for example.
Captcha Properties
These are the effective parameter values for the current instance – values configured in the CaptchaConfig.asp file are used as application defaults, and values set in ASP form source are used to override these defaults. The combination of those two sets of values is the actual state of the Captcha object, displayed in the "Captcha control info" section of troubleshooting output.
A Note About Randomization
If you are randomizing Captcha properties such as the image style used (as is recommended), the values displayed in troubleshooting info might not match the values used for actual Captcha image or sound generation. This behavior is by design. For example:
- If you choose the image style randomly from 10 possible values, one of them will be chosen when the
Captchaobject is created on page load, and displayed for troubleshooting. - Since the Captcha image is loaded in a Http request separate from the main form access, a new
Captchainstance will be created then, and the image style used for image generation will be chosen again from all possible values.
[back to Troubleshooting info legend]
Persisted Captcha Paramters for the Current Captcha ID
Since application default Captcha parameters are kept in the CaptchaConfig.asp file as explained above, we need to keep ASP form overrides for each Captcha object in ASP Session state.
As you can see in the screenshot above, only those values that differ from the application defaults are actually kept in Session state.
[back to Troubleshooting info legend]
Persisted Captcha Codes for the Current Captcha ID
These are the actual Captcha codes, stored in ASP Session state. Each code also keeps track of its generation time, to allow setting Captcha code timeouts (so the Captcha can only be validated within 5 minutes, for example).
- Reloading the Captcha image (using the reload icon) changes the Captcha code and refreshes the timeout, while re-using the Instance ID.
- Validating the Captcha (successfully or unsuccessfully) deletes the Captcha code (you will notice the Instance ID for the validated code disappearing from the list) and generates a new instance (with its own Captcha code) on page reload.
- Reloading the page without submitting it (or opening it in a new browser tab) adds a new Instance ID to the collection, while keeping the old ones intact. This allows cross-tab validation to work, and each form access to be properly recorded for Captcha purposes.
Please Note
The information on this page applies to a discontinued version of BotDetect™ ASP CAPTCHA (v4.x)
Current BotDetect Versions
-
BotDetect ASP.NET CAPTCHA
2019-07-22v4.4.2 -
BotDetect Java CAPTCHA
2019-07-22v4.0.Beta3.7 -
BotDetect PHP CAPTCHA
2019-07-22v4.2.5